The digital spine of Britain's energy system
We’re working alongside our partners to make Britain more connected, so we can all lead smarter, greener lives. There are millions of smart meters connected to the DCC’s secure network, bringing consumers and energy suppliers closer to their data. But how do smart meters work? How do they send readings? Who can access the data?
Step by step
How smart meters send data to energy suppliers
Using energy in your home
Every time energy is used or generated in a home with a smart meter, it is turned into a packet of data. The data is securely wrapped, using two layers of encryption, and a communications hub creates a home area network to receive it.
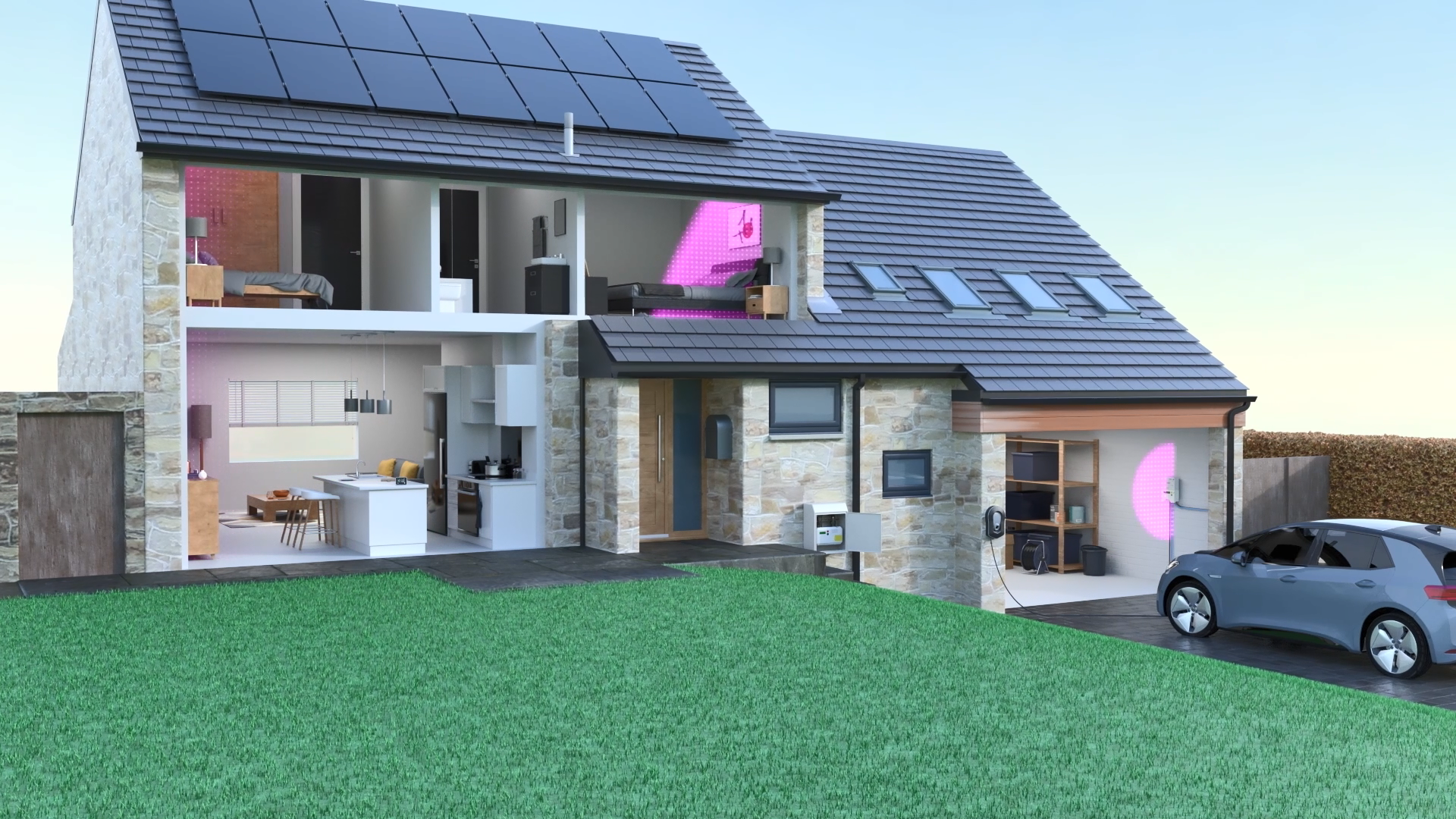


From your home to the DCC
The communications hub transmits the data to an in-home display which shows how much energy is being used or sold back to the grid. Your smart meter readings are then transmitted from the home to a wide area network (made up of mobile phone or radio masts), and from these to the DCC servers.
Our secure digital highway
Our Security and Technical Operations Centre is the nerve centre of the DCC network. Here our team continually monitor the performance, resilience, speed and security of the network. The DCC network never sees or keeps the data, it transports it securely straight to the energy supplier. They decrypt the data and use it to bill consumers accurately.
What messages are sent across the smart meter network?
The DCC network supports almost 150 different types of messages, including service requests and alerts. Some of the most common messages include:

Prepayment
The prepayment service allows end consumers to add credit to their meters through an over-the-air top-up over our network, keeping the lights on for millions of people. This service is the most critical that DCC provides, supporting some of the most vulnerable consumers in the country.
Install and commission
The install and commission service allows new smart meters to be installed within homes and then join the DCC network. This provides the end consumer with full smart functionality and the benefits that come with that.
Change of energy supplier
For smart meters on the DCC network there is full interoperability between energy suppliers meaning the meter does not need to be replaced when switched. The Change of Supplier service allows fast, simple switching between energy suppliers for end consumers.
Meter reads
The most utilised message on the DCC network is meter reads allowing energy suppliers to remotely read energy usage and remove the need for a regular house visit or manual meter readings by consumers. The service provides frequent, accurate billing of energy at the time of use and is one of the main benefits of having a smart meter.

Firmware
The firmware service allows for remote upgrades of meters unlocking new functionality and benefits as innovation is created.
Smart meter data defined
At the simplest level, smart meter data is commonly described as either ‘message contents’ or ‘system data’. A letter sent by post provides a useful analogy to explain the difference.
The letter
The message content sent to or from devices connected to the system within premises, eg the amount of energy consumed (consumption data) or amount added to a prepayment meter.

The envelope
System data or information about the message, eg where it was sent and to which device, at what time and whether it arrived safely.

How can your smart meter help you reduce your carbon footprint?
Smart gas and electricity meters provide incredible insights into how much energy you're using at any given time and can help identify how you might lower your usage and bills.
Find out more
SMETS1 and SMETS2 smart meters
What are SMETS1 smart meters and how are they different from SMETS2 meters?
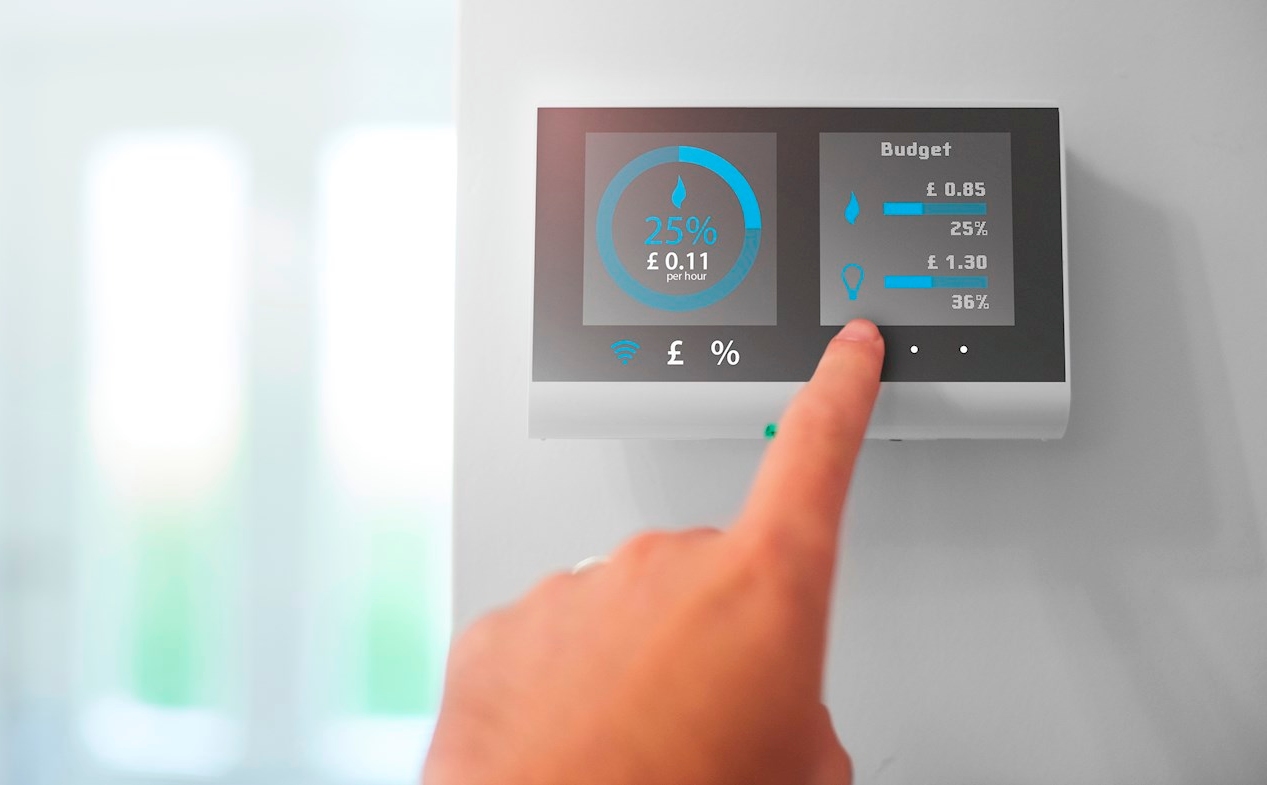

Your smart meter in-home display
What is an in-home display and how can you use it to understand your energy usage?
Protecting data on the smart meter network
The smart meter network, designed with security at its core, operates entirely separately from the potential pitfalls of the public internet and operates to security levels endorsed by the National Cyber Security Centre, part of GCHQ.

Smart Energy GB
Smart Energy GB is the not-for-profit campaign helping everyone in Britain understand the importance of smart meters and their benefits to people and the environment.

Further reading


