Martin Brown, Senior Vice President of Consulting Services at CGI Consulting, shares his thoughts on our recent 10 million milestone. Having been one of the pioneering forces behind CGI's Instant Energy System, an earlier mode of communication between smart meters using the mobile phone network, Martin knows a thing or two about smart meters and the undeniable benefits they have for society.
The early days of Instant Energy
Back in 2006, when I was a Project Manager working on an Energy Trading project, we ran a little experiment. We asked a sample of CGI Group employees in the UK to stand outside a dumb meter with their mobile phones to see if they could send and receive text messages. The logic behind this rudimental survey was that if we could demonstrate that cellular coverage could reach a big enough percentage of meters, we could invest in building a communication system using the mobile phone network. As it turned out, cellular coverage could reach a considerable number of meters, which allowed us to create our Instant Energy system.
By 2019 and at its peak, there were 4 million first generation smart meters installed on Instant Energy, all communicating using the mobile phone network. Many of those gas and electricity smart meters have now been migrated onto the DCC's systems. For those not familiar with the terminology, a smart meter becomes dormant, when it stops returning smart metering data. This happens when one changes to an energy supplier that is not connected to the Instant Energy system. Now, thanks to this migration, first generation smart meters can link up with any supplier via the DCC’s systems and be smart again.
Smart Meters & Hair Straighteners
Personally, I was an early adopter of gas and electricity smart meters, getting my energy supplier to install what I now realise was a pre-SMETS1 smart meter. While this meant the meter could not be migrated to the DCC, it provided my family and I with an In-Home Display. We used to spend our time tracking down heavy use electrical appliances (hair straighteners were a particular favourite), switching to LED bulbs in order to avoid the IHD moving from green (low usage) to red (high usage). This, combined with a couple of weekends spent adding more insulation to the loft, saw our energy bills drop considerably. But I wanted to do more.
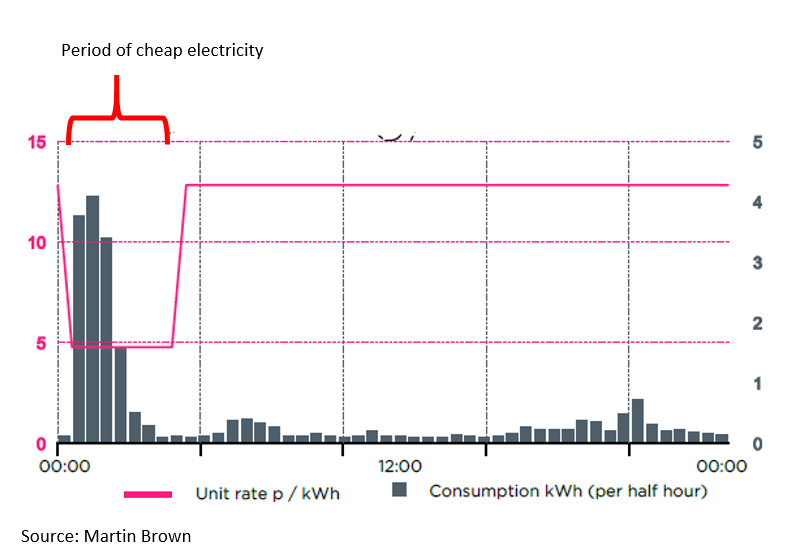
So, I had an early second generation smart meter installed, which opened up a new world of energy savings for us and reduced our energy bills. We purchased an electric car and signed up to a ‘time of use tariff' to get electricity at a third of the normal price for 4 hours overnight. My smart meter sends back each half hour’s consumption to my energy supplier; from the graph below, you can see that we use most of our electricity in those four hours on a typical day.
My wife is a doctor and continued to drive to work every day during the first lockdown. She drove 8,000 miles last year. Charging the car, running the dishwasher and washing machine on timers in total cost us £125 for the entire year. Without Smart Metering, none of this would have been possible.
The role of the Data Service Provider
I am very proud to lead a team of consultants, technology and industry experts at CGI Group who are playing a key role in this transformation. We came a long way from the Instant Energy days and when in 2013, DCC awarded us the Data Services Provider (DSP) contract, putting us at the heart of Great Britain’s Smart Metering central system.
The DSP is a system designed to operate at scale. To help visualise this, if we took every smart meter installed on the system today and put them in a line, they would stretch from London to Rome. To deliver this, we have built a system consisting of 2.5 million java code lines and over 400 servers, routers, firewalls; and processing 15 million transactions every day. Our team supports the current service by developing and testing each new functionality before it is deployed and has worked on 343 major changes over the life of the service.
On a typical day, energy suppliers install 18,000 gas and electricity smart meters using a large field force of engineers in customers' homes. Our work focuses on avoiding outages to the system that would leave thousands of engineers unable to work and customers waiting for their smart meters to be installed. Using the ELK Elastic Stack, we monitor 755 processes in real-time. Our team operates 24x7 to proactively pick up on problems and ensure they are dealt with before they have the opportunity to become critical.
Security is also paramount. Since the system went live, our Security Operations Centre has reviewed over 300 billion log files looking for possible cyber threats to the system. In doing so, we keep a log of every message that has ever passed through the system (upwards of 23 billion) and provide regular users reports on this data.
On top of this, we also help the DCC to coordinate a complex environment of service providers to ensure a seamless delivery into both the different test and production environments. We operate in 25 separate data centres across the entire DCC ecosystem, with many moving parts to synchronise, a typical month may see around two hundred changes in the production environment.
At CGI, we are very proud of the key role we play in supporting the Britain’s smart meter Infrastructure and the impact that this will have in all our futures.
CGI Group are a leading systems integration, business process services and consulting services firm and a DCC service provider.

Martin Brown
Senior Vice President of Consulting Services at CGI
Useful documents
Further reading